USC Viterbi Professor Assad Oberai has developed a machine learning algorithm that could make breast cancer diagnosis more accurate. PHOTO/ANDRESR, ISTOCK
Have you ever felt a lump in your breast? The odds are someone in your life has or will. Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death among women. It is also difficult to diagnose. Nearly one in 10 cancers is misdiagnosed as not cancerous, meaning that a patient can lose critical treatment time. On the other hand, the more mammograms a woman has, the more likely it is she will see a false positive result. After 10 years of annual mammograms, roughly two out of three patients who do not have cancer will be told that they do and be subjected to an invasive intervention, most likely a biopsy.
Breast ultrasound elastography is an emerging imaging technique that provides information about a potential breast lesion by evaluating its stiffness in a non-invasive way. Using more precise information about the characteristics of a cancerous versus non-cancerous breast lesion, this methodology has demonstrated more accuracy compared to traditional modes of imaging.
At the crux of this procedure, however, is a complex computational problem that can be time-consuming and cumbersome to solve. But what if instead we relied on the guidance of an algorithm?
Assad Oberai, USC Viterbi Hughes Professor in the Department of Aerospace and Mechanical Engineering, asked this exact question in the research paper, “Circumventing the solution of inverse problems in mechanics through deep learning: application to elasticity imaging,” published in ScienceDirect. Along with a team of researchers, including USC Viterbi Ph.D student Dhruv Patel, Oberai specifically considered the following: Can you train a machine to interpret real-world images using synthetic data and streamline the steps to diagnosis? The answer, Oberai says, is most likely yes.
In the case of breast ultrasound elastography, once an image of the affected area is taken, the image is analyzed to determine displacements inside the tissue. Using this data and the physical laws of mechanics, the spatial distribution of mechanical properties—like its stiffness—is determined. After this, one has to identify and quantify the appropriate features from the distribution, ultimately leading to a classification of the tumor as malignant or benign. The problem is the final two steps are computationally complex and inherently challenging.
In his research, Oberai sought to determine if they could skip the most complicated steps of this workflow entirely. Cancerous breast tissue has two key properties: heterogeneity, which means some areas are soft and some are firm, and non-linear elasticity, which means the fibers offer a lot of resistance when pulled instead of the initial give associated with benign tumors. Knowing this, Oberai created physics-based models that showed varying levels of these key properties. He then used thousands of data inputs derived from these models in order to train the machine learning algorithm.
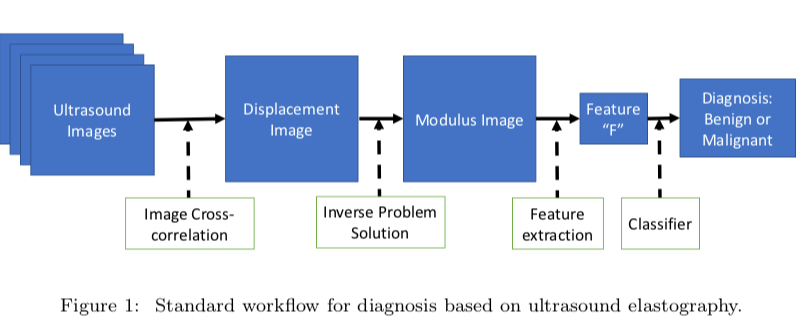
PHOTO/COURTESY ASSAD OBERAI
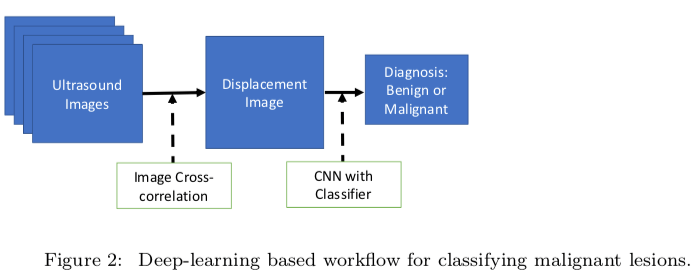
PHOTO/COURTESY ASSAD OBERAI
Synthetic Versus Real-World Data
But why would you use synthetically-derived data to train the algorithm? Wouldn’t real data be better?
“If you had enough data available, you wouldn’t,” said Oberai. “But in the case of medical imaging, you’re lucky if you have 1,000 images. In situations like this where data is scarce, these kinds of techniques become important.”
Oberai and his team used about 12,000 synthetic images to train their machine learning algorithm. This process is similar in many ways to how photo identification software works, learning through repeated inputs how to recognize a particular person in an image, or how our brain learns to classify a cat versus a dog. Through enough examples, the algorithm is able to glean different features inherent to a benign tumor versus a malignant tumor and make the correct determination.
Oberai and his team achieved nearly 100 percent classification accuracy on other synthetic images. Once the algorithm was trained, they tested it on real-world images to determine how accurate it could be in providing a diagnosis, measuring these results against biopsy-confirmed diagnoses associated with these images.
“We had about an 80 percent accuracy rate. Next, we continue to refine the algorithm by using more real-world images as inputs,” Oberai said.
Changing How Diagnoses are Made
There are two prevailing points that make machine learning an important tool in advancing the landscape for cancer detection and diagnosis. First, machine learning algorithms can detect patterns that might be opaque to humans. Through manipulation of many such patterns, the algorithm can produce an accurate diagnosis. Secondly, machine learning offers a chance to reduce operator-to-operator error.
So then, would this replace a radiologist’s role in determining diagnosis? Definitely not. Oberai does not foresee an algorithm that serves as a sole arbiter of cancer diagnosis, but instead, a tool that helps guide radiologists to more accurate conclusions. “The general consensus is these types of algorithms have a significant role to play, including from imaging professionals whom it will impact the most. However, these algorithms will be most useful when they do not serve as black boxes,” said Oberai. “What did it see that led it to the final conclusion? The algorithm must be explainable for it to work as intended.”
Adapting the Algorithm for Other Cancers
Because cancer causes different types of changes in the tissue it impacts, the presence of cancer in a tissue can ultimately lead to a change in its physical properties, for example a change in density or porosity. These changes are can be discerned as a signal in medical images. The role of the machine learning algorithm is to pick out this signal and use it to determine whether a given tissue that is being imaged is cancerous.
Using these ideas, Oberai and his team are working with Vinay Duddalwar, professor of clinical radiology at the Keck School of Medicine of USC, to better diagnose renal cancer through contrast enhanced CT images. Using the principles identified in training the machine learning algorithm for breast cancer diagnosis, they are looking to train the algorithm on other features that might be prominently displayed in renal cancer cases, such as changes in tissue that reflect cancer-specific changes in a patient’s microvasculature, the network of microvessels that help distribute blood within tissues.
Published on July 9th, 2019
Last updated on July 12th, 2019